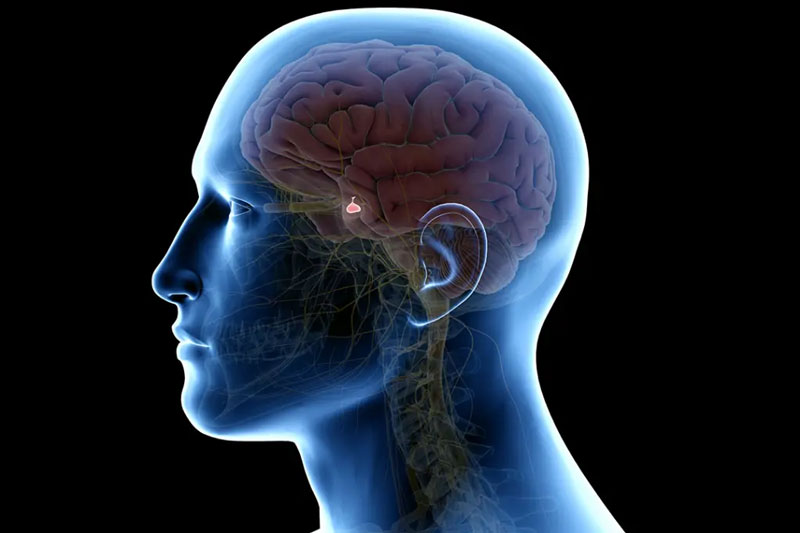
What is a Pituitary Adenoma?
A pituitary adenoma is a non-cancerous (benign) tumor that develops in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate various body functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Pituitary adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor. They are usually slow-growing and may not cause any symptoms for years. However, as they grow, they can put pressure on the surrounding tissues and structures, including the optic nerves, which can lead to vision problems.
Pituitary adenomas are classified according to the type of hormone they produce. Some tumors produce hormones that can cause a wide range of symptoms, including abnormal growth, changes in menstrual cycles, and changes in the body’s metabolism. Other tumors are non-functional, meaning they do not produce hormones and may not cause any symptoms until they grow large enough to press on surrounding tissues.
What Causes Pituitary Adenoma?
The exact cause of pituitary adenomas is not fully understood. However, there are some factors that may increase the risk of developing these tumors, including:
- Genetic mutations: In some cases, genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing pituitary adenomas. These mutations can be inherited or acquired during a person’s lifetime.
- Age: Pituitary adenomas are more common in people over the age of 50.
- Gender: Certain types of pituitary adenomas, such as prolactinomas, are more common in women.
- Previous radiation exposure: Radiation exposure to the head and neck area may increase the risk of developing pituitary adenomas.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), may increase the risk of developing pituitary adenomas.
It’s important to note that many people with pituitary adenomas have no identifiable risk factors, and the vast majority of pituitary adenomas are non-cancerous and slow-growing.

Symptoms of Pituitary Adenoma
The symptoms of a pituitary adenoma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the type of hormone it produces. Some common symptoms may include:
- Headaches: Pituitary adenomas can cause headaches that are often described as dull and persistent.
- Vision problems: As the tumor grows, it can put pressure on the optic nerves, causing vision problems such as blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision.
- Hormone excess or deficiency: Pituitary adenomas can produce hormones that disrupt the body’s normal hormonal balance, leading to symptoms such as:
-
- – Excessive thirst and urination
-
- – Abnormal menstrual cycles
-
- – Erectile dysfunction or decreased libido
-
- – Growth abnormalities, such as acromegaly (enlargement of the hands, feet, and facial features)
-
- – Cushing’s disease, which can cause weight gain, high blood pressure, and other symptoms
-
- – Fatigue and weakness
It’s important to note that many people with pituitary adenomas have no symptoms and may only discover the tumor incidentally during medical imaging. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, particularly if you have vision problems or hormone excess or deficiency, you should talk to your doctor.
-
Treatment Options for Pituitary Adenoma
The treatment options for pituitary adenoma depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the symptoms it’s causing. Some treatment options include:
- Observation: In some cases, a small pituitary adenoma that’s not causing any symptoms may simply be monitored with regular imaging to check for any changes in size or growth and lab tests to monitor hormones.
- Medications: Certain medications can be used to shrink or control the growth of pituitary adenomas. For example, certain medications can decrease an elevated prolactin level and cause the prolactin-producing pituitary adenoma to shrink.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor may be recommended, especially for larger pituitary adenomas or those that are causing vision problems. Surgery is typically done using a minimally invasive technique called transsphenoidal surgery, which involves accessing the tumor through the nose.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used to shrink or destroy pituitary adenomas that cannot be removed surgically, or to treat residual tumor cells after surgery.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the symptoms it’s causing, the age and overall health of the patient, and the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the best treatment approach for your specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Pituitary Adenoma
Are all pituitary tumors benign?
Malignant pituitary tumors are extremely rare. In fact, over 99 percent of pituitary tumors are benign.
How do I know if my pituitary adenoma is making hormones?
Blood tests to check for hormone excess or deficiency can help identify whether the pituitary adenoma is making hormones.
What kind of imaging do I need to check my pituitary gland?
An MRI scan of the brain dedicated to evaluating the pituitary gland is the ideal imaging study.