
More than 2 out of 5 adults in the United States live with obesity—the exact prevalence was 41.9% based on data from 2017 – 20201. Many struggling with the difficulty of weight loss and weight maintenance opt for different diets and exercise plans. Some are labeled “medical weight loss” plans, but often are cookie-cutter approaches with little supporting evidence. A personalized medical weight loss program created by an obesity medicine certified physician can lead to real, sustainable results. In this article, we explain medical weight loss, how it works, and who is a candidate for such a program.
What is Obesity?
Before explaining medical weight loss, it is important to understand obesity and eliminate a common misconception. Obesity is a complex, chronic disease involving an excess accumulation of adipose tissue (body fat)2. The physical stress and associated inflammation of excess adipose tissue increase the risk of developing conditions such as osteoarthritis, high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
Obesity is NOT the result of lack of discipline or poor choices. There are several biological processes that work against an individual’s efforts to lose and maintain their weight.
What is Medical Weight Loss?
Medical weight loss is the use of non-surgical methods for achieving weight loss, such as nutrition, physical activity, behavior modification, and/or prescription medications. A common approach for goal-setting is to “lose x pounds.” We advocate reframing a pound-based weight loss goal to percent body weight loss. There are excellent data showing improvement in blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar beginning at 5% body weight loss. In individuals with prediabetes, 7% – 10% body weight loss is effective for preventing progression to diabetes3. 5% – 10% body weight loss will decrease the liver’s fat content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease4. Percent body weight loss is a more meaningful biomarker than the number of pounds lost, as it provides insight into treatment of the complications of obesity, as shown in the figure below.
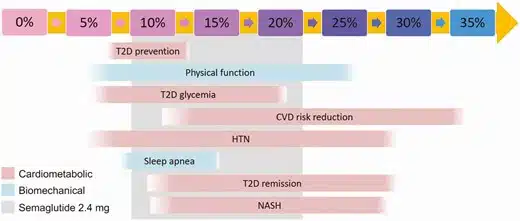
Role of Body Composition
There is a pitfall of percent body weight loss as a biomarker. How do we know how much weight lost is excess fat vs lean mass (particularly muscle mass)? The ultimate goal of a medical weight program is loss of excess fat with minimal loss of muscle mass. Medical body composition analyzes this difference. The different methods for assessing body composition include skinfold measurement, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), air displacement, bioelectrical impedance, etc. Regardless of technique, there is tremendous value in knowing baseline body fat percentage and muscle mass, and then tracking changes in composition over time to guide fat loss and minimize muscle loss.
How Does Medical Weight Loss Work?
Initial Consultation
The process for medical weight loss at Ethos Endocrinology begins with scheduling an initial consultation. Upon scheduling and receiving a confirmation, our team releases a weight history questionnaire in your personal portal account. This electronic questionnaire can be completed from the comfort of home or work and takes only 10 minutes to complete. Questions include current and previously tried eating patterns and medications, barriers with progress, level of physical activity, sleep hygiene, and mental health. The questionnaire is reviewed in detail prior to your arrival and serves as the foundation for the 1-hour consultation.
Dr. Kanji builds on this information with questions to understand your specific concerns and struggles. He evaluates your medical history in detail and assesses eligibility for weight loss medication. This is followed by a physical exam, and a medical body composition measurement (image of device below) to serve as the baseline for your weight loss journey. Dr. Kanji reviews your baseline body composition report with you. The consultation concludes with recommended lab tests to evaluate your metabolic and hormone health. Following the initial consultation, 2 documents are uploaded to your portal account:
- A copy of your body composition report
- A customized handout describing the various weight loss medications to guide your selection.

2-Week Follow-up
The first follow-up visit is approximately 2 weeks after your initial consultation and can be completed in-office or virtually based on need and preference. Lab results are reviewed with you by Dr. Kanji. Then your personalized plan is discussed. The overall goal of your plan is loss of excess fat while minimizing muscle loss.
Your personalized plan includes:
1) Nutrition: Customized calorie and protein targets based on your body composition
2) Physical activity: Tailored based on your current level with the eventual goal of incorporating resistance movements to minimize muscle loss
3) Medication: Options are reviewed and Dr. Kanji will guide medication selection based on medical history, your preferences/concerns, and cost/insurance coverage
Months 1-6
Active weight loss usually occurs in the first 6 months but may take up to 1 year. During this phase, follow-up visits will be monthly. Follow-up visits vary between office and virtual, depending on the need for repeat body composition analysis. During each follow-up visit, nutrition, physical activity, and medication are reviewed and adjusted as necessary.
Months 6-12+
After transitioning to the maintenance phase, follow-up visits gradually decrease in frequency to every 2 months and eventually every 3 months. The maintenance phase can be more challenging than the active loss phase, and it is purposely dynamic in follow-up frequency. For example, some individuals require periods of time with increased follow-up frequency to monthly to prevent excess regain. Once weight is stabilized again, follow-ups are decreased back to every 2 or 3 months. During maintenance visits, nutrition, physical activity, and medication are reviewed.
Am I a Candidate for Medical Weight Loss?
You may be a candidate for medical weight loss if you have struggled with losing weight or maintaining weight loss. For use of weight loss medication, one of the following criteria must be met:
- Body Mass Index (BMI) ≥ 30kg/m2
- BMI ≥ 27kg/m2 with the presence of a weight-related condition, such as high blood pressure, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus, elevated cholesterol, heart disease, obstructive sleep apnea, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), etc.
- Body fat percentage ≥ 32% for women
- Body fat percentage ≥ 25% for men
Selecting a Medical Weight Loss Program
The excess accumulation of adipose tissue (body fat) in obesity increases the risk of negative health effects. Losing this excess fat, minimizing muscle loss, and maintaining it is the ultimate goal—not just decreasing the number on the scale. It is important to select a medical weight loss program that understands this goal and has an obesity medicine certified physician to create a personalized plan for you. Schedule your consultation to begin your journey to lose excess fat, keep muscle, and gain health.




